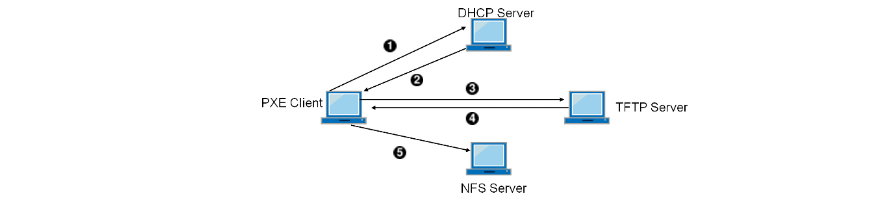
This tutorial is to showcase unattended and automatic install of multiple CentOS 6.5 x86_64 Hadoop nodes pre-configured with Ambari-agents and an Ambari-server host.
After configuring automatic install of bare metal (No OS pre-installed) nodes, deploying a Hadoop cluster will be a matter of clicks. The setup uses:
- PXE boot (for automatic OS install)
- TFTP server (for PXE network install image)
- Apache server (to serve the kickstart file for
unattended install) - DHCP server (for assigning IP addresses for the
nodes) - DNS server (for internal domain name resolution)
- Puppet-master (for automatic configuration management
of all hosts in the network, Ambari install included in Puppet
manifests) - Ambari-master and agents (for managing Hadoop
ecosystem deployment)
The setup assumes that the nodes are on the 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0 network, the master is on 192.168.0.1 and its hostname is bigdata1.hdp
The domain for the network server by the configuration is hdp and
the clients are named as bigdata[1-254].hdp
Master Server
- Install CentOS 6.5 X86_64
manually- CentOS-6 updates until November 30, 2020
- Install guide
- Configure network
- dnsmasq
- Install and configure dnsmasq providing a basic DHCP, DNS and TFTP server. Easily configurable, ideal for internal networks
yum install dnsmasq
-
- /etc/dnsmasq.conf
- DHCP setup
- DNS setup
- TFTP setup
- /etc/dnsmasq.conf
#DNS domain-needed bogus-priv domain=hdp expand-hosts local=/hdp/ listen-address=127.0.0.1 listen-address=192.168.0.1 #Local interface interface=p4p1 #DHCP dhcp-range=p4p1,192.168.0.100,192.168.0.200 #set default gateway dhcp-option=p4p1,3,192.168.0.1 #DNS servers server=192.168.0.1 server=8.8.8.8 #TFTP enable-tftp tftp-root=/var/lib/tftpboot dhcp-boot=pxelinux.0 #Reserved IPs+MAC addresses will get added here by our custom script
- TFTP PXE boot files at /var/lib/tftpboot downloadable with the package above, containing
- Linux image
- Kickstart file
- Note config parameters below
- Root password for each client will be hadoop135
- Note config parameters below
# NFS server, CentOS image at /var/nfs install nfs --server 192.168.0.1 --dir /var/nfs # Lang and keyboard lang en_US.UTF-8 selinux --enforcing keyboard us skipx # Network network --bootproto dhcp --hostname bigdatax.hdp # Root pw. is hadoop135 rootpw --iscrypted $1$wHydp2Aq$KmJuQFeHYTe8fMsV2tUga. # Allow SSH firewall --service=ssh authconfig --useshadow --passalgo=sha256 --kickstart timezone --utc UTC # Configure services, add extra repos, Epel services --disabled autofs,gpm,sendmail,cups,iptables,ip6tables,auditd,arptables_jf,xfs,pcmcia,isdn,rawdevices,hpoj,bluetooth,openibd,avahi-daemon,avahi-dnsconfd,hidd,hplip,pcscd,restorecond,mcstrans,rhnsd,yum-updatesd repo --name="Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux" --mirrorlist=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-6&arch=x86_64 bootloader --location=mbr --append="nofb quiet splash=quiet" zerombr clearpart --all --initlabel autopart text reboot # Add Packages %packages --ignoremissing yum dhclient ntp wget mc @Core epel-release puppet %end %post --nochroot exec < /dev/tty3 > /dev/tty3 #changing to VT 3 so that we can see whats going on.... /usr/bin/chvt 3 ( cp -va /etc/resolv.conf /mnt/sysimage/etc/resolv.conf /usr/bin/chvt 1 ) 2>&1 | tee /mnt/sysimage/root/install.postnochroot.log %end %post logger "Starting anaconda bigdatax.hdp postinstall" exec < /dev/tty3 > /dev/tty3 # Changing to VT 3 so that we can see whats going on.... /usr/bin/chvt 3 ( # Update local time echo "updating system time" /usr/sbin/ntpdate -sub 0.fedora.pool.ntp.org /usr/sbin/hwclock --systohc # Update all the base packages from the updates repository yum -t -y -e 0 update # And add the puppet package yum -t -y -e 0 install puppet echo "Configuring puppet" cat > /etc/puppet/puppet.conf << EOF [main] vardir = /var/lib/puppet logdir = /var/log/puppet rundir = /var/run/puppet ssldir = $vardir/ssl [agent] pluginsync = true report = true ignoreschedules = true daemon = false ca_server = epmhubd1.hdp certname = epmhubdx.hdp environment = ambari_dev server = epmhubd1.hdp EOF # Setup Puppet to run on system reboot /sbin/chkconfig --level 345 puppet on # Register Puppet, download config files /usr/bin/puppet agent --config /etc/puppet/puppet.conf -o --tags no_such_tag --server bigdata1.hdp --no-daemonize sync %end
- Install Apache
yum install httpd
-
- Move Kickstart default file to /var/www/html/kickstart
- Start Apache
- Check if kickstart is available at http://bigdata1.hdp/kickstart
- Install NFS
yum install nfs-utils nfs-utils-lib
-
- Edit /etc/exports and point it to your NFS shared folder
- In our case /var/nfs
- Download the CentOS 6.5 x86_64 DVD ISO Image to
this location from here: http://wiki.centos.org/Download
- Edit /etc/exports and point it to your NFS shared folder
- Puppet master setup
- Puppet provisioning settings originally from
- https://blog.codecentric.de/en/2014/04/hadoop-cluster-provisioning/
- Modified repository information
- Puppet classes sets
- NTP Clock Sync
- Host information
- Installs Ambari Agents with node specific hostname settings
- https://blog.codecentric.de/en/2014/04/hadoop-cluster-provisioning/
- Puppet provisioning settings originally from
node 'bigdata2.hdp' { # VM-Configuration of an ambari agent that is monitored by the ambari server. # Turn off interfering services include interfering_services # Install and enable ntp include ntp # Ensure that servers can find themselves even in absence of dns class { 'etchosts': ownhostname => 'bigdata2.hdp' } class { 'ambari_agent': serverhostname => "bigdata1.hdp", ownhostname => "bigdata2.hdp" } # Establish ordering Class['interfering_services'] -> Class['ntp'] -> Class['etchosts'] -> Class['ambari_agent'] }
- IPtables configuration for Internet sharing, DHCP,
TFTP, DNS- Edit /etc/sysctl.conf add net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
for allowing Net interface MASQ to Loc (internet connection sharing from internet network interface to local – needed for getting Ambari Repos) - Ensure that all ports configured below have running services and are accessible – otherwise install of hosts won’t work
- Edit /etc/sysctl.conf add net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward # wlan0 is the external network, p4p1 is the lan, internal network iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o wlan0 -j MASQUERADE iptables -A FORWARD -i wlan0 -o p4p1 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -i p4p1 -o wlan0 -j ACCEPT # allow TFTP iptables -A INPUT -i p4p1 -s 192.168.0.0/24 -p udp --dport 69 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # allow DHCP iptables -A INPUT -i p4p1 -s 192.168.0.0/24 -p udp --dport 67:68 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # allow DNS iptables -A INPUT -i p4p1 -s 192.168.0.0/24 -p udp --dport 53 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # allow NFS iptables -A INPUT -i p4p1 -s 192.168.0.0/24 -p tcp --dport 1025 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # allow HTTP iptables -A INPUT -i p4p1 -s 192.168.0.0/24 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT service iptables save service iptables restart
- Custom script to add a new host
-
- A simple and not too elegant Bash script to add a new host
- Remark: checking input format, hostname as parameter, removing a host is a future task, still it works as-is
- ./script.sh 00:11:22:33:44:55 96 parameter is the MAC
address of a client - Steps
- Reads the MAC and Counter values from counter.txt in the same directory (counter = 192.168.0.counter value of machine name and IP)
- Adds MAC and IP to /etc/dnsmasq.conf to have a fixed, DHCP assigned IP address
- Adds the node’s hostname to /etc/hosts file for DNS to work (dnsmasq DNS server reads entries from there)
- Adds a TFTP entry with the MAC address for PXE boot to
/var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/-01-mac - Adds the Kickstart file to /var/www/html with modified host and IP data for unattended install
- Adds Puppet config files to /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp for the specific node to intall NTP and Ambari-agent on the node
- Increments Counter for the next host
- A simple and not too elegant Bash script to add a new host
#/bin/bash if [ $# -eq 0 ] then printf "Need a MAC address in format 00-11-22-33-44-55" fi macdash=$1 macpoint=`printf $macdash | sed 's/-/:/g'` #This is to store the end of IP address of range 192.168.0.0 / 255.255.255.0 var=`cat counter.txt` # Modify dnsmasq.conf printf " #bigdata`echo $var` " >> /etc/dnsmasq.conf printf "dhcp-host=`echo $macpoint`,192.168.0.`echo $var`" >> /etc/dnsmasq.conf # Modify hosts printf " 192.168.0.`echo $var` bigdata`echo $var`.hdp" >> /etc/hosts # Add MAC to TFTP /bin/cp -rf /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/copy /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/01-`echo $macdash` sed "s/kickstart/kickstart$var/g" /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/01-`echo $macdash` > /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/`echo $macdash`_tmp mv -f /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/`echo $macdash`_tmp /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/01-`echo $macdash` # Add Kickstart file /bin/cp -rf /var/www/html/kickstart /var/www/html/kickstart`echo $var` sed "s/bigdatax/bigdata$var/g" /var/www/html/kickstart`echo $var` > /var/www/html/kickstart`echo $var`_tmp mv -f /var/www/html/kickstart`echo $var`_tmp /var/www/html/kickstart`echo $var` # Modify Puppet Manifest printf " node 'bigdata`echo $var`.hdp' { " >> /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp printf " include interfering_services include ntp " >> /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp printf " class { 'etchosts': ownhostname => 'bigdata`echo $var`.hdp' } " >> /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp printf " class { 'ambari_agent': serverhostname => "bigdata1.hdp", ownhostname => "bigdata`echo $var`.hdp" } " >> /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp printf " Class['interfering_services'] -> Class['ntp'] -> Class['etchosts'] -> Class['ambari_agent'] }" >> /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp # Restart service dnsmasq restart var=$((var+1)) printf $var > counter.txt
Clients
Clients automatically installs on boot from network interface if their MAC address have been added to the system by using the above script. Select Boot media: PXE boot when starting the machine.
Provisioning
- Use Puppet manifests: http://docs.puppetlabs.com/learning/
- For configuration management of your hosts. With Puppet you can batch apply system configurations and send commands to your hosts.
- Current script installs Ambari-Agent
- SSH login is available
Install Hadoop (with Ambari)
Install Ambari-Server and Agent on the master host computer with pre-configured Puppet Manifest
- Edit /etc/puppet/environments/ambari_dev/manifest/one.pp in
case default hostnames need to be changed - Run to configure Ambari repository
puppet apply /etc/puppet/environments/ambari_dev/manifest/one.pp-
- Setup and start Ambari
ambari-server setup ambari-server start
-
-
- Point your browser to http://bigdata1.hdp:8080
- Log in to the Ambari Server using the default username/password: admin/admin.
-
- Install
-
This guide will not detail Ambari and Hadoop settings. A default install
will put together a cluster of Hadoop.
Ambari Tutorial

- Open browser on bigdata1:8080

- Choose HDP’s version (HDP 2.1) and repository of your OS (Centos6 will use Redhat6 repo)

- Add your hosts, you can use regular expressions like bigdata[0-200].hdp, choose manual registration as Ambari-Agents are already installed

- Ambari will recognize all Agents in case those are properly installed and network with DNS is configured by using Dnsmasq as above

- Pre-deploy screens assesses confronting packages and issues that might cause errors

- Choose the Hadoop components to be deployes on your clusters

- Assign masters for the services of your cluster

- Assign slaves and clients for the services of your cluster

- Parse through settings
- Settings that must be changed are highlighted with red

- Review the deployment of your cluster
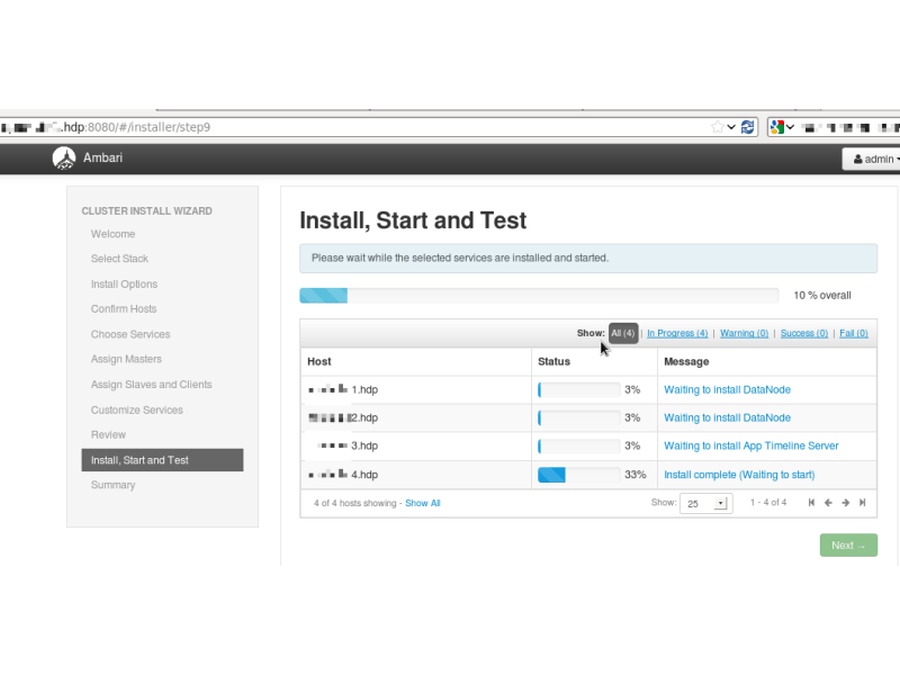
- Be patient for the deploy. It may be restarted if there are failures.

- Services will get started up after the deploy

- Deploy finished with no errors

- Post deploy screen shows problems and error logs and a summary on the install process (hosts and services)

- Ambari uses Nagios for comprehensive monitoring with an easy-to-use Hadoop cluster monitoring dashboard that shows usage and status of each services
Troubleshooting Hadoop deployment, cluster
- Kickstart’s last lines might fail to run
- Check if Puppet is installed
- Check Puppet configuration /etc/puppet/puppet.conf both
- On master
- If autosign is on for new clients in the network
- And on child nodes
- If server and certificates are configured in the [agent] section
- On master
- Puppet master won’t start
- Check Puppet certificates on child nodes with
- puppet agent –test
- Check Puppet certificates on child nodes with
- Fail to load Ambari on localhost:8080
- Check if Ambari is installed and running
- Check if Ambari Agent is set on nodes with server attribute at /etc/ambari-agent/conf
- SSL cert problem is common: check if the certificates corresponds each other on master and agent, if those are not revoked or out of valid dateframe due to clock sync problems
- Check Ambari logs on master and agents too, if there are any SQL
errors, reinstall if any
- Fail to register Ambari-Agents
- Update OpenSSL
- Check if /etc/ambari-agent
config files have correct server settings - Check /var/log/ambari-agent/ logs
- Always check all outputs of the custom script adding machines by using
their MAC address- If dnsmasq is altered at /etc/dnsmasq.conf
- Regarding DHCP
- If tftpboot contains the MAC address at PXEboot
- If the webserver has a corresponding kickstartx file and the
webserver itself is accessible by the clients - If Puppet has an entry for the new node on configuration
- If dnsmasq is altered at /etc/dnsmasq.conf
- Can’t access services of master
- Check IPTables from remote nodes: web server, TFTP, DNS, DHCP ports
are open and working - Check DNS resolution by pinging nodes from other nodes
- Check IPTables from remote nodes: web server, TFTP, DNS, DHCP ports
- SSL certificate problems are common in Puppet and Ambari (which uses
another instance of Puppet)- Check if NTP is running
- Regenerate certificates for masters and agents
- In case of any problem
- Check if all services are up and running
- Check network configuration
- Check if services are accessible from agent nodes
- Always check logs
-
- /var/log/puppet
- /var/log/ambari-server
- /var/log/ambari-agent
- /var/log/messages
- /var/log/[hadoop services]